Pack
A pack is a program that performs an analysis on a data source. Packs are executed by agents according to routines. Its purpose is to process the source and retrieve useful information about it to send back to the platform.
How to Create a 'Pack'?
Create a Pack
- Command
- Result
qalita pack init --name my_pack
>>> qalita pack init --name my_pack
Created package folder: my_pack_pack
Created file: properties.yaml
Created file: pack_conf.json
Created file: main.py
Please update the main.py file with the required code
Created file: run.sh
Please update the run.sh file with the required commands
Created file: requirements.txt
Please update the requirements.txt file with the required package dependencies
Created file: README.md
Please READ and update the README.md file with the description of your pack
This creates a my_pack_pack folder with the following files:
my_pack_pack
├── main.py
├── pack_conf.json
├── properties.yaml
├── README.md
├── requirements.txt
└── run.sh
The most important files are run.sh and properties.yaml, which are essential. Before each pack publication, a check for the existence of these files is systematically performed.
| File | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| main.py | Contains the pack code | main.py |
| pack_conf.json | Contains the pack configuration | pack_conf.json |
| properties.yaml | Contains the pack properties | properties.yaml |
| README.md | Contains the pack description | README.md |
| requirements.txt | Contains the pack dependencies | requirements.txt |
| run.sh | Is the entry point of the pack | run.sh |
To see templates and examples of packs, you can refer to the public GitHub repository.
Test a Pack
You can test your pack locally before publishing it to the platform.
To do this, you need to use the Qalita CLI:
qalita pack validate -n my_pack
qalita pack run -n my_pack
If you want to use the pack locally on data, please create a temporary source_conf.json file.
Example with a local dataset:
{
"config": {
"path": "~/data/heart"
},
"description": "11 clinical features for predicting heart disease events.",
"id": 6,
"name": "Heart Failure Prediction Dataset",
"owner": "aleopold",
"owner_id": 2,
"reference": false,
"sensitive": false,
"type": "file",
"validate": "valid",
"visibility": "internal"
}
Remember to delete the result files, logs, source configuration file, and cache files before publishing your pack.
During Execution
The entry point of the pack is the run.sh file, located in the root path of the temporary local folder created by the agent.
run.sh Example:
#/bin/bash
python -m pip install --quiet -r requirements.txt
python main.py
The pack is fed by a source_conf.json file and, if the pack is of type compare, an additional target_conf.json file.
These files contain the config: data of the source.
These files are located next to the entry point run.sh.
source_conf.json Example:
{
"config": {
"path": "/home/lucas/desktop"
},
"description": "Desktop files",
"id": 1,
"name": "local_data",
"owner": "lucas",
"type": "file",
"reference": false,
"sensitive": false,
"visibility": "private",
"validate": "valid"
}
The pack is responsible for managing its own source type compatibility by checking the type of the source in the source_conf.json file.
After Execution
At the end of the pack execution, the agent looks for:
logs.txt: A file uploaded to provide feedback logs to the platform in the frontend.
logs.txt Example:
2023-07-21 11:51:12,688 - qalita.commands.pack - INFO - ------------- Pack Run -------------
2023-07-21 11:51:15,087 - qalita.commands.pack - INFO - CSV files found:
2023-07-21 11:51:15,222 - qalita.commands.pack - ERROR - Summarize dataset: 0%| | 0/5 [00:00` ?, ?it/s]
...
Visible on the platform:
recommendations.json
The Recommendations file contains the recommendations given by the pack about the source.
recommendations.json Example:
{
[
{
"content": "Cholesterol has 172 (18.7%) zeros",
"type": "Zeros",
"scope": {
"perimeter": "column",
"value": "Cholesterol"
},
"level": "info"
},
{
...
}
...
]
}
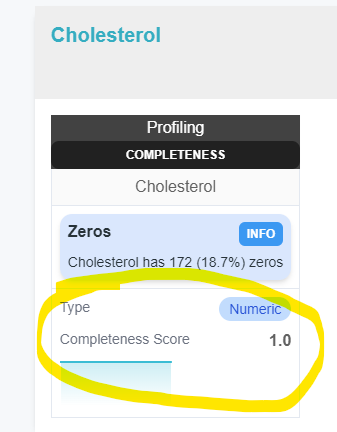
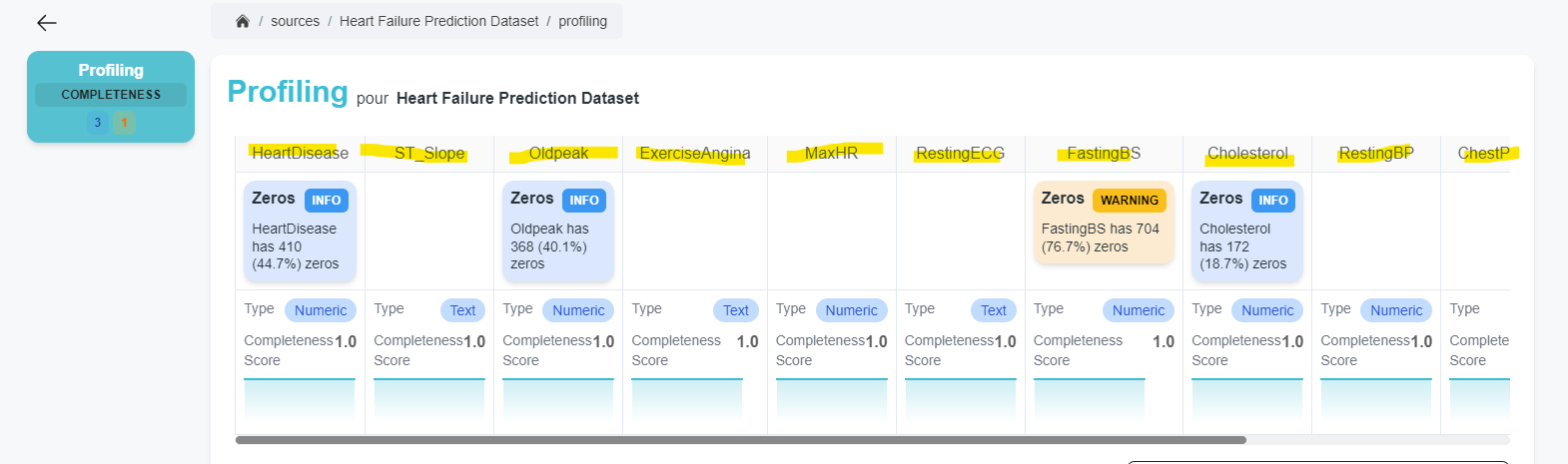
The recommendations are then materialized in the pack view on the source page.
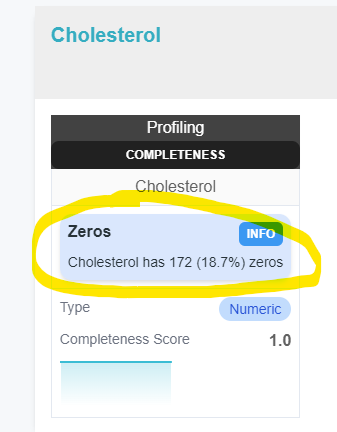
There are several levels of recommendations level:
info: Informationwarning: Warninghigh: High
metrics.json
The Metrics file contains the metrics given by the pack about the source.
metrics.json Example:
{
[
{
"key": "types_numeric",
"value": "7",
"scope": {
"perimeter": "dataset",
"value": "Heart Failure Prediction Dataset"
}
},
{
"key": "is_unique",
"value": "0",
"scope": {
"perimeter": "column",
"value": "Age"
}
},
{
...
}
...
]
}
The metrics are then materialized in the pack view on the source page.
The metrics and recommendations are sent to the platform and are then available for the pack execution view of the source.
schemas.json
The Schemas file contains the schemas given by the pack about the source.
schemas.json Example:
[
{
"key": "dataset",
"value": "Heart Failure Prediction Dataset",
"scope": {
"perimeter": "dataset",
"value": "Heart Failure Prediction Dataset"
}
},
{
"key": "column",
"value": "Age",
"scope": {
"perimeter": "column",
"value": "Age"
}
},
{
"key": "column",
"value": "Sex",
"scope": {
"perimeter": "column",
"value": "Sex"
}
},
....
]
The schemas are then materialized in the pack view on the source page.
Publish a Pack
Packs have authors; you can only publish a pack if you are the author. You can see the author of a pack on the pack page:
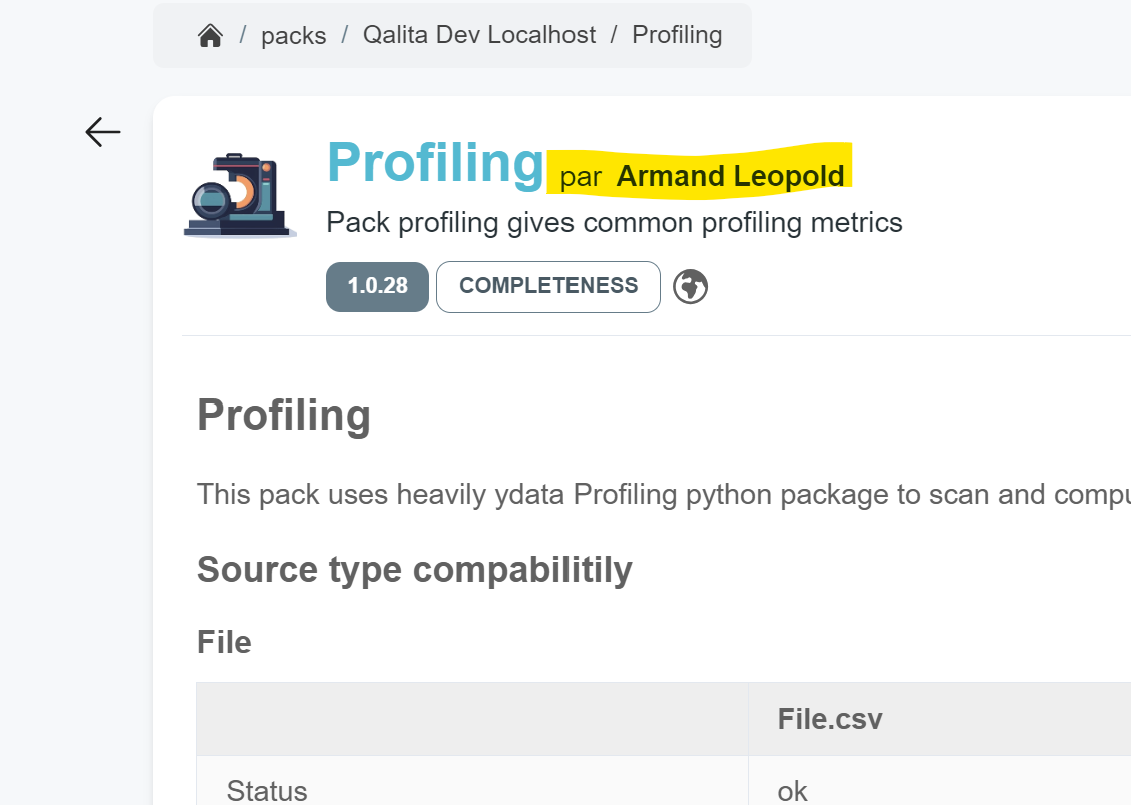
Viewing the author of a pack
When adding partners, their public packs will be accessible to you in another tab on the packs page of the application.
They will also be listed using qalita pack list, and you can use them like any other pack.
However, you will not be able to modify them.
The author of these packs will be the "partner" user created when the partner was added.
To publish a pack, you need to use the Qalita CLI:
- Install the Qalita CLI
pip install qalita
- Retrieve your API token from your profile page
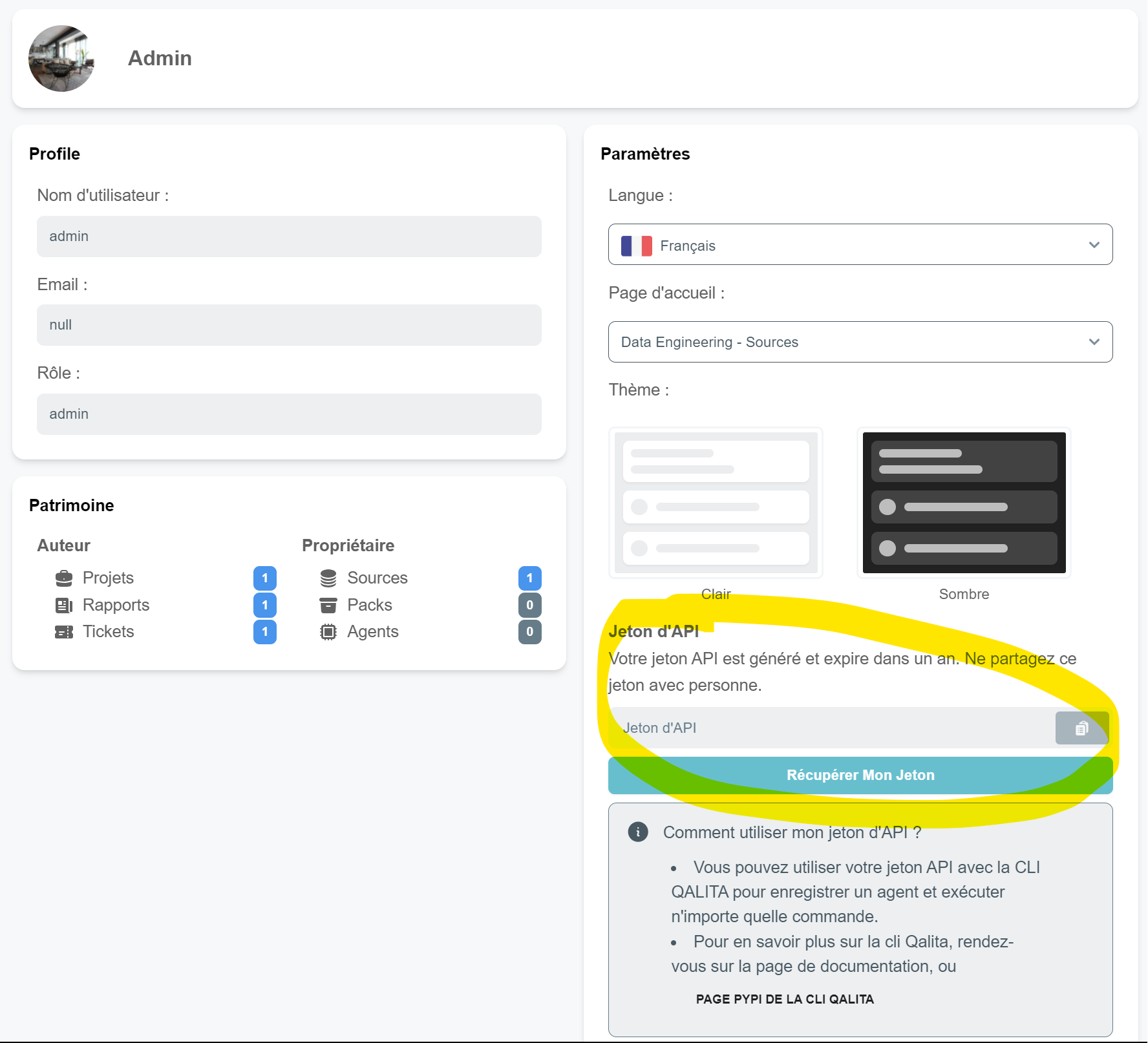
- Log in to the platform
agentName=admin
fileName="$HOME/.qalita/.env-$agentName"
mkdir -p $(dirname $fileName)
echo "QALITA_AGENT_NAME=$agentName" > $fileName
echo "QALITA_AGENT_MODE=worker" >> $fileName
echo "QALITA_AGENT_ENDPOINT=http://localhost:3080" >> $fileName
echo "QALITA_AGENT_TOKEN=" >> $fileName
- Navigate to the parent folder of the pack
Example for a pack named my-pack:
/-- parent-folder <----- here
|-- my-pack_pack
| |-- __init__.py
| |-- my-pack.py
- Publish the pack
- Command
- Result
qalita pack push -n my_pack
>>> qalita pack push -n my_pack
------------- Pack Validation -------------
Pack [my_pack] validated.
------------- Pack Push -------------
Pack [my_pack] published
New pack version [1.0.0] detected. Pushing pack version
Pack [my_pack] updated successfully
Pack asset uploaded
Pack pushed!
You can then find your pack on the platform:
Qalita Pack Assistant
You can use our conversational bot Qalita Pack Assistant to assist you in creating packs.
Our bot benefits from a specific knowledge base for creating Qalita packs. It will guide you and optimize your productivity.

Public QALITA Packs
You can find public Qalita packs on our GitHub repository. These packs are maintained by QALITA SAS and the community. All contributions are appreciated.